Stores the incoming message data as attribute data of the message originator.
Preconditions
The node accepts messages of type POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST and expects message data to be a JSON object where each property name represents an attribute key, and its corresponding
value is the attribute value. For example:
1
2
3
4
{
"firmware_version": "1.0.1",
"serial_number": "SN-001"
}
Configuration
Processing settings
The save attributes node can perform three distinct actions, each governed by configurable processing strategies:
- Attributes: saves attribute data to the database.
- WebSockets: notifies WebSocket subscriptions about updates to the attribute data.
- Calculated fields: notifies calculated fields about updates to the attribute data.
For each of these actions, you can choose from the following processing strategies:
- On every message: perform the action for every incoming message.
- Deduplicate: groups messages from each originator into time intervals and only performs the action only for the first message within each interval.
Duration of the interval is specified by Deduplication interval setting.
To determine the interval a message falls within, the system calculates a deduplication interval number using the following formula:
1
long intervalNumber = ts / deduplicationIntervalMillis;
Where:
tsis the timestamp used for deduplication (in milliseconds).deduplicationIntervalMillisis the configured Deduplication interval (converted automatically to milliseconds).intervalNumberdetermines the logical time bucket the message belongs to.
The timestamp
tsis determined using the following priority:- If the message metadata contains a
tsproperty (in UNIX milliseconds), it is used. - Otherwise, the time when the message was created is used.
All timestamps are UNIX milliseconds (in UTC).
Example
With a 60-second deduplication interval:
- Device sends messages at 10:00:15, 10:00:45, and 10:01:10
- The first two messages (10:00:15 and 10:00:45) fall in the same interval - only the message at 10:00:15 is processed
- The message at 10:01:10 falls in the next interval, so it gets processed
- Skip: never perform the action.
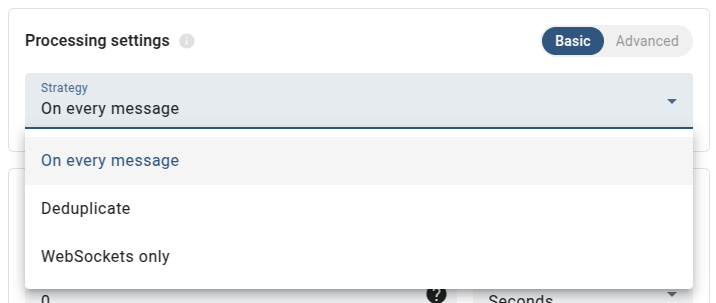
Processing strategies can be set using either Basic or Advanced processing settings.

- Basic processing settings - provide predefined strategies for all actions:
- On every message: applies the On every message strategy to all actions. All actions are performed for all messages.
- Deduplicate: applies the Deduplicate strategy (with a specified interval) to all actions.
- WebSockets only: for all actions except WebSocket notifications, the Skip strategy is applied, while WebSocket notifications use the On every message strategy. Effectively, nothing is stored in a database; data is available only in real-time via WebSocket subscriptions.
- Advanced processing settings - allow you to configure each action’s processing strategy independently.
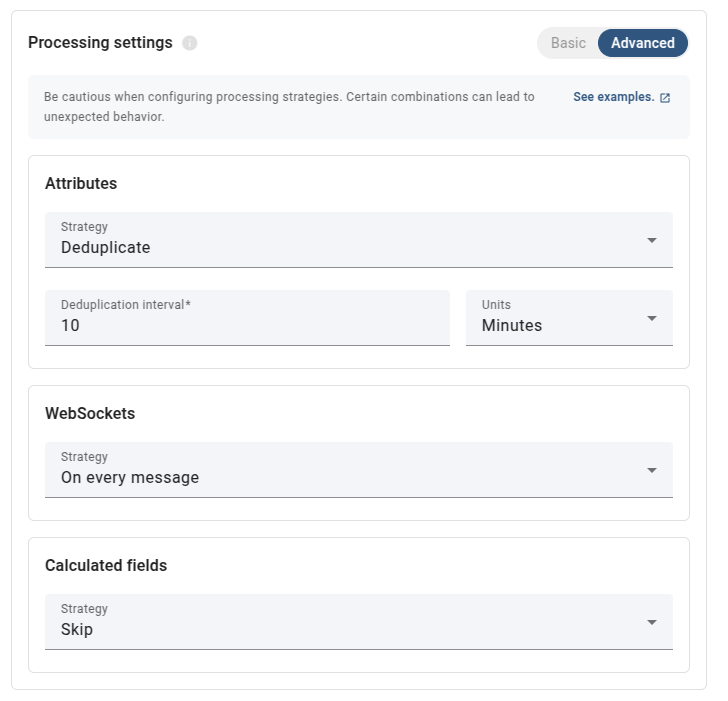
When configuring the processing strategies in advanced mode, certain combinations can lead to unexpected behavior. Consider the following scenarios:
-
Skipping database storage
Choosing to disable one or more persistence actions (for instance, skipping database storage for Time series or Latest values while keeping WS updates enabled) introduces the risk of having only partial data available:
- If a message is processed only for real-time notifications (WebSockets) and not stored in the database, historical queries may not match data on the dashboard.
- When processing strategies for Time series and Latest values are out-of-sync, telemetry data may be stored in one table (e.g., Time series) while the same data is absent in the other (e.g., Latest values).
-
Disabling WebSocket (WS) updates
If WS updates are disabled, any changes to the time series data won’t be pushed to dashboards (or other WS subscriptions). This means that even if a database is updated, dashboards may not display the updated data until browser page is reloaded.
-
Skipping calculated field recalculation
If telemetry data is saved to the database while bypassing calculated field recalculation, the aggregated value may not update to reflect the latest data. Conversely, if the calculated field is recalculated with new data but the corresponding telemetry value is not persisted in the database, the calculated field’s value might include data that isn’t stored.
-
Different deduplication intervals across actions
When you configure different deduplication intervals for actions, the same incoming message might be processed differently for each action. For example, a message might be stored immediately in the Time series table (if set to On every message) while not being stored in the Latest values table because its deduplication interval hasn’t elapsed. Also, if the WebSocket updates are configured with a different interval, dashboards might show updates that do not match what is stored in the database.
-
Deduplication cache clearing
The deduplication mechanism uses an in-memory cache to track processed messages by interval. This cache retains up to 100 intervals for a maximum of 2 days, but entries may be cleared at any time due to its use of soft references. As a result, deduplication is not guaranteed, even under light loads. For example, with a deduplication interval of one day and messages arriving once per hour, each message may still be processed if the cache is cleared between arrivals. Deduplication should be treated as a performance optimization, not a strict guarantee of single processing per interval.
-
Whole message deduplication
It’s important to note that deduplication is applied to the entire incoming message rather than to individual time series keys. For example, if the first message contains key A and is processed, and a subsequent message (received within the deduplication interval) contains key B, the second message will be skipped—even though it includes a new key. To safely leverage deduplication, ensure that your messages maintain a consistent structure so that all required keys are present in the same message, avoiding unintended data loss.
Due to the scenarios described above, the ability to configure each persistence action independently—including setting different deduplication intervals—should be treated as a performance optimization rather than a strict processing guarantee.
Scope
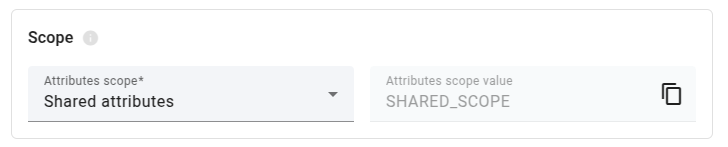
The node supports three attribute scopes: Client attributes, Shared attributes, and Server attributes. You can set the default scope in the node configuration, or override it
by specifying a valid scope property in the message metadata.
The supported scope values are:
CLIENT_SCOPEcorresponds to Client attributesSHARED_SCOPEcorresponds to Shared attributesSERVER_SCOPEcorresponds to Server attributes
If the message metadata contains an invalid scope (e.g. INVALID_SCOPE) value, the message processing will fail.
Advanced settings
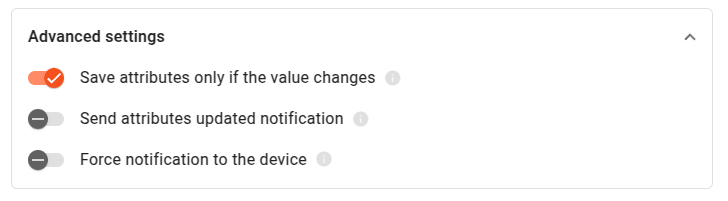
- Save attributes only if the value changes – if enabled, the node compares incoming attributes with their current stored values and only saves attributes that are new, have changed values, or have different data types.
- Send attributes updated notification – if enabled, the node sends an Attributes Updated
event to the originator’s default rule chain for
SHARED_SCOPEandSERVER_SCOPEattributes. - Force notification to the device - if enabled, the node always sends attribute update notifications to devices with active subscriptions. If disabled, device notifications
are controlled by the
notifyDeviceproperty in the message metadata (defaults totruewhen absent).
JSON Schema
Message processing algorithm
-
The node verifies that the message type is
POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST. If not, the processing fails and the message is routed to theFailureconnection. -
The node parses the message data to extract attribute key-value pairs. If the data is empty, the processing ends and message is routed to the
Successconnection. - The node determines the attribute scope using the following priority:
- Message metadata
scopeproperty value, if present and valid (CLIENT_SCOPE,SHARED_SCOPE, orSERVER_SCOPE) - If an invalid scope (e.g.
INVALID_SCOPE) is provided in metadata, processing fails and the message is routed to theFailureconnection. - Node’s configured default scope, if metadata scope value is not provided
- Message metadata
- If Save attributes only if the value changes is enabled, the node performs change detection:
- Retrieves current attribute values for all incoming attribute keys from the database
- Compares each incoming attribute with its current stored value
- Filters the attributes list to include only those that:
- Are new (not currently stored)
- Have different values from what’s currently stored
- Have different data types from what’s currently stored
- If no changes are detected, the processing ends and the message is routed to the
Successconnection.
- The node determines device notification settings using the following priority:
- Always notify if Force notification to the device is enabled in configuration
- Otherwise, check the message metadata
notifyDeviceproperty:- If absent or empty string: defaults to sending notification
- If present: sends notification only if the value is
true(case-insensitive)
- Saves the attributes to the database according to the configured processing strategy. Once the save operation completes:
- On success: the processing is successful and the message is routed to the
Successconnection - On failure: the processing fails and the message is routed to the
Failureconnection - If Send attributes updated notification was enabled, an
ATTRIBUTES_UPDATEDevent is published to the originator default rule chain forSHARED_SCOPEandSERVER_SCOPEattributes.
- On success: the processing is successful and the message is routed to the
Output connections
Success- If an incoming message was successfully processed.
Failure- If an incoming message type is not
POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST. - If an incoming message payload cannot be parsed to attribute key-value pairs.
- If the incoming message metadata includes a non-empty
scopeproperty whose value does not match one of the valid attribute scopes (i.e.CLIENT_SCOPE,SHARED_SCOPE, orSERVER_SCOPE). - If unexpected error occurs during message processing.
- If an incoming message type is not
Examples
Example 1 — On every message strategy
Incoming message
Type: POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST
Originator: DEVICE
Data:
1
2
3
4
5
{
"firmware_version": "1.0.1",
"serial_number": "SN-001",
"last_maintenance": "2025-01-15"
}
Node configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
{
"scope": "SERVER_SCOPE",
"notifyDevice": false,
"sendAttributesUpdatedNotification": true,
"updateAttributesOnlyOnValueChange": false,
"processingSettings": {
"type": "ON_EVERY_MESSAGE"
}
}
Outgoing message
The outgoing message is identical to the incoming one. Routed via the Success connection.
Result
Three server attributes are saved:
firmware_version: “1.0.1”serial_number: “SN-001”last_maintenance: “2025-01-15”
WebSocket subscriptions and calculated fields are notified. An ATTRIBUTES_UPDATED event is sent to the originator’s default rule chain since the scope is SERVER_SCOPE.
Example 2 — Attributes with Deduplicate strategy
Incoming message
Type: POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST
Originator: DEVICE
Data:
1
2
3
4
5
{
"battery_level": 85,
"signal_strength": -65,
"location": "Building A, Floor 2"
}
Node configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
"scope": "CLIENT_SCOPE",
"notifyDevice": true,
"sendAttributesUpdatedNotification": false,
"updateAttributesOnlyOnValueChange": false,
"processingSettings": {
"type": "DEDUPLICATE",
"deduplicationIntervalSecs": 120
}
}
State of the system
Message for this device that falls within current 120-second interval was already processed.
Outgoing message
The outgoing message is identical to the incoming one. Routed via the Success connection.
Result
Since deduplication is enabled with a 120-second interval and the message was already processed, the attributes are not saved to the database. WebSocket notifications and calculated fields are also not triggered.
Example 3 — Advanced processing with mixed strategies
Incoming message
Type: POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST
Originator: DEVICE
Data:
1
2
3
4
5
{
"cpu_usage": 45.7,
"memory_usage": 78.2,
"disk_usage": 62.5
}
Node configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
{
"scope": "SHARED_SCOPE",
"notifyDevice": false,
"sendAttributesUpdatedNotification": true,
"updateAttributesOnlyOnValueChange": false,
"processingSettings": {
"type": "ADVANCED",
"attributes": {
"type": "DEDUPLICATE",
"deduplicationIntervalSecs": 300
},
"webSockets": {
"type": "ON_EVERY_MESSAGE"
},
"calculatedFields": {
"type": "SKIP"
}
}
}
State of the system
Message for this device that falls within current deduplication interval was already processed.
Outgoing message
The outgoing message is identical to the incoming one. Routed via the Success connection.
Result
- Attributes are NOT saved to the database due to deduplication
- WebSocket subscriptions ARE notified
- Calculated fields are NOT triggered (SKIP strategy)
- An
ATTRIBUTES_UPDATEDevent is NOT sent since attributes weren’t saved
Example 4 — Save attributes only if value changes
Incoming message
Type: POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST
Originator: DEVICE
Data:
1
2
3
4
5
{
"temperature_threshold": 25.0,
"humidity_threshold": 70.0,
"maintenance_scheduled": true
}
Node configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
{
"scope": "SERVER_SCOPE",
"notifyDevice": false,
"sendAttributesUpdatedNotification": true,
"updateAttributesOnlyOnValueChange": true,
"processingSettings": {
"type": "ON_EVERY_MESSAGE"
}
}
State of the system
Current stored attributes:
temperature_threshold: 25.0 (same value)humidity_threshold: 65.0 (different value)maintenance_scheduled: not stored (new attribute)
Outgoing message
The outgoing message is identical to the incoming one. Routed via the Success connection.
Result
Only two attributes are saved due to change detection:
humidity_threshold: 70.0 (value changed from 65.0)maintenance_scheduled: true (new attribute)
The temperature_threshold is not saved since its value hasn’t changed. WebSocket subscriptions and calculated fields are notified only for the changed attributes.
Example 5 — Scope override from message metadata
Incoming message
Type: POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST
Originator: DEVICE
Data:
1
2
3
{
"power_setting": "low"
}
Metadata:
1
2
3
{
"scope": "CLIENT_SCOPE"
}
Node configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
{
"scope": "SERVER_SCOPE",
"notifyDevice": false,
"sendAttributesUpdatedNotification": true,
"updateAttributesOnlyOnValueChange": false,
"processingSettings": {
"type": "ON_EVERY_MESSAGE"
}
}
Outgoing message
The outgoing message is identical to the incoming one. Routed via the Success connection.
Result
One client attributes is saved (using scope from metadata):
power_setting: “low”
No ATTRIBUTES_UPDATED event is sent since client attributes don’t trigger this notification.