- Prerequisites
- Step 1. Install Java 17 (OpenJDK)
- Step 2. ThingsBoard service installation
- Step 3. Configure ThingsBoard database
- Step 4. Choose ThingsBoard queue service
- Step 5. [Optional] Memory update for slow machines (4GB of RAM)
- Step 6. Run installation script
- Step 7. Start ThingsBoard service
- Post-installation steps
- Troubleshooting
- Windows firewall settings
- Next steps
Prerequisites
This guide describes how to install ThingsBoard on a Windows machine. Instructions below are provided for Windows 11/10. Hardware requirements depend on chosen database and amount of devices connected to the system. To run ThingsBoard and PostgreSQL on a single machine you will need at least 4Gb of RAM. To run ThingsBoard and Cassandra on a single machine you will need at least 8Gb of RAM.
Step 1. Install Java 17 (OpenJDK)
ThingsBoard service is running on Java 17. Follow this instructions to install OpenJDK 17.
- Visit Open JDK Download Page. Go to “Other platforms and versions”, select “Operating System” as “Windows”, “Architecture” as “x64”, “Version” as “17 - LTS” and download JDK .msi package.
- Run the downloaded MSI package and follow the instructions. Make sure you have selected “Add to PATH” and “Set JAVA_HOME variable” options to “Will be installed on local hard drive” state.
- Visit PostgreSQL JDBC Download Page to download PostgreSQL JDBC Driver. Choose the latest available option.
- Create the folder C:\Program Files\JDBC and copy downloaded file there. Then, add a new global variable - run PowerShell as an administrator and execute the following command. Do not forget to change “postgresql-42.2.18.jar” in the command to match the downloaded version.
1
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("CLASSPATH", '.;"C:\Program Files\JDBC\postgresql-42.2.18.jar"', [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)
You can check the installation using the following command (using Command Prompt):
1
java -version
Expected command output is:
1
2
3
4
C:\Users\User>java -version
openjdk version "17.x.xx"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment Temurin-17.x.xx (...)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM Temurin-17.x.xx (...)
Step 2. ThingsBoard service installation
Download and extract the package.
1
https://github.com/thingsboard/thingsboard/releases/download/v4.3.0.1/thingsboard-windows-4.3.0.1.zip
Note: We assume you have extracted ThingsBoard package to default location: C:\Program Files (x86)\thingsboard
Step 3. Configure ThingsBoard database
ThingsBoard is able to use SQL or hybrid database approach. See corresponding architecture page for more details.
PostgreSQL InstallationDownload the installation file (PostgreSQL 15 or newer releases) here and follow the installation instructions. During PostgreSQL installation, you will be prompted for superuser (postgres) password. Don’t forget this password. It will be used later. For simplicity, we will substitute it with “postgres”. Create ThingsBoard DatabaseOnce installed, launch the “pgAdmin” software and login as superuser (postgres). Open your server and create database “thingsboard” with owner “postgres”. ThingsBoard ConfigurationIn case you have specified the PostgreSQL superuser password as “postgres”, you can skip this step. Open the Notepad or other editor as administrator user (right click on the app icon and select “Run as administrator”). and locate “# SQL DAO Configuration” block. Don’t forget to replace “postgres” with your real postgres user password: locate “SQL_POSTGRES_TS_KV_PARTITIONING” parameter in order to override the default value for timestamp key-value storage partitioning size: |
Step 4. Choose ThingsBoard queue service
ThingsBoard platform currently supports two type of messaging brokers for storing the messages and communication between ThingsBoard services: In-memory and Kafka-based brokers.
-
In Memory queue implementation is built-in and default. It is useful for development(PoC) environments and is not suitable for production deployments or any sort of cluster deployments.
-
Kafka is recommended for production deployments. This queue is used on the most of ThingsBoard production environments now. It is useful for both on-prem and private cloud deployments. It is also useful if you like to stay independent from your cloud provider. However, some providers also have managed services for Kafka. See AWS MSK for example.
-
Confluent Cloud is a fully managed streaming platform based on Kafka. Useful for a cloud agnostic deployments.
See corresponding architecture page and rule engine page for more details.
In Memory queue is built in and enabled by default. No additional configuration is required. |
Kafka InstallationApache Kafka is an open-source stream-processing software platform. Install KafkaUse the instructions below for installing Kafka in a Docker container. Add the following lines to the docker-compose-kafka.yml file: Start the container: ThingsBoard ConfigurationOpen the Notepad or other editor as administrator user (right click on the app icon and select “Run as administrator”). and locate “queue:” block. Make sure the queue type is “kafka”, and don’t forget to replace “localhost:9092” with your real Kafka bootstrap servers: |
Confluent Cloud ConfigurationTo access Confluent Cloud you should first create an account, then create a Kafka cluster and get your API Key. ThingsBoard ConfigurationOpen the Notepad or other editor as administrator user (right click on the app icon and select “Run as administrator”). and locate “queue:” block. Make sure the queue type is “kafka”, replication factor is “3” and use confluent cloud is “true”. Don’t forget to replace “CLUSTER_API_KEY”, “CLUSTER_API_SECRET” and “localhost:9092” with your real Confluent Cloud bootstrap servers: These params affect the number of requests per second from each partitions per each queue. Number of requests to particular Message Queue calculated based on the formula: ((Number of Rule Engine and Core Queues) * (Number of partitions per Queue) + (Number of transport queues) + (Number of microservices) + (Number of JS executors)) * 1000 / POLL_INTERVAL_MS For example, number of requests based on default parameters is: Rule Engine queues: Main 10 partitions + HighPriority 10 partitions + SequentialByOriginator 10 partitions = 30 Core queue 10 partitions Transport request Queue + response Queue = 2 Rule Engine Transport notifications Queue + Core Transport notifications Queue = 2 Total = 44 Number of requests per second = 44 * 1000 / 25 = 1760 requests Based on the use case, you can compromise latency and decrease number of partitions/requests to the queue, if the message load is low. By UI set the parameters - interval (1000) and partitions (1) for Rule Engine queues. Sample parameters to fit into 10 requests per second on a “monolith” deployment: You can update default Rule Engine queues configuration using UI. More about ThingsBoard Rule Engine queues see in documentation. |
Step 5. [Optional] Memory update for slow machines (4GB of RAM)
Open the Notepad or other editor as administrator user (right click on the app icon and select “Run as administrator”).
Open the following file for editing (select “All Files” instead of “Text Documents” in file choosing dialog, the encoding is UTF-8):
1
C:\Program Files (x86)\thingsboard\thingsboard.xml
Locate the following lines to the configuration file.
1
2
<startargument>-Xms512m</startargument>
<startargument>-Xmx1024m</startargument>
and change them to
1
2
<startargument>-Xms2048m</startargument>
<startargument>-Xmx2048m</startargument>
change “2048m” to approximately 1/3rd of your total RAM (in MB)
Step 6. Run installation script
Launch windows shell (Command Prompt) as Administrator. Change directory to your ThingsBoard installation directory.
Execute install.bat script to install ThingsBoard as a Windows service (or run ”.\install.bat –loadDemo” to install and add demo data). This means it will be automatically started on system startup. Similar, uninstall.bat will remove ThingsBoard from Windows services. The output should be similar to this one:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
C:\Program Files (x86)\thingsboard>.\install.bat --loadDemo
Detecting Java version installed.
CurrentVersion 170
Java 17 found!
Installing thingsboard ...
...
ThingsBoard installed successfully!
Step 7. Start ThingsBoard service
Now let’s start the ThingsBoard service! Open the command prompt as an Administrator and execute the following command:
1
net start thingsboard
Expected output:
1
2
The ThingsBoard Server Application service is starting.
The ThingsBoard Server Application service was started successfully.
In order to restart the ThingsBoard service you can execute following commands:
1
2
net stop thingsboard
net start thingsboard
Once started, you will be able to open Web UI using the following link:
1
http://localhost:8080/
The following default credentials are available if you have specified –loadDemo during execution of the installation script:
- System Administrator: sysadmin@thingsboard.org / sysadmin
- Tenant Administrator: tenant@thingsboard.org / tenant
- Customer User: customer@thingsboard.org / customer
You can always change passwords for each account in account profile page.
Post-installation steps
Upgrading to new ThingsBoard version
Keep Your Platform Secure and Up-to-Date
When a new ThingsBoard release becomes available, we provide a streamlined update process to ensure your system benefits from the latest features and security patches without any risk to your data.
Please refer to our official Upgrade Instructions for detailed steps tailored to your current deployment environment.
Troubleshooting
The log files are located in logs folder (“C:\Program Files (x86)\thingsboard\logs” in our case).
The thingsboard.log file should contain following line:
1
YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss,sss [main] INFO o.t.s.ThingsboardServerApplication - Started ThingsboardServerApplication in x.xxx seconds (JVM running for x.xxx)
In case of any unclear errors, use general troubleshooting guide or contact us.
Windows firewall settings
In order to have external access to ThingsBoard Web UI and device connectivity (HTTP, MQTT, CoAP) you need to create a new inbound rule with Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
- Open “Windows Firewall” from “Control Panel”:
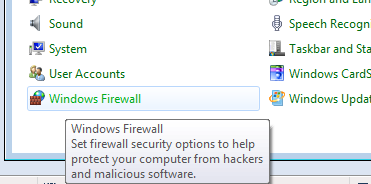
- Click “Advanced settings” on the left panel:
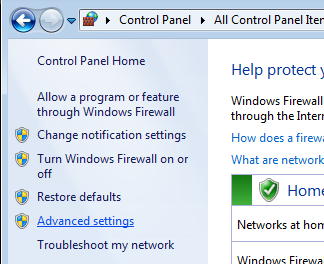
- Select “Inbound Rules” on the left panel, then click “New Rule…” on the right “Actions” panel:
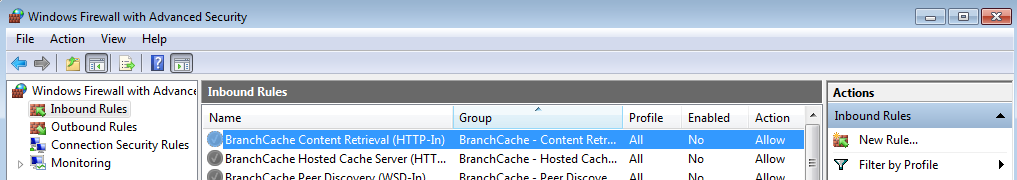
- Now new “New Inbound Rule Wizard” window will open. On the first step “Rule Type” select “Port” option:
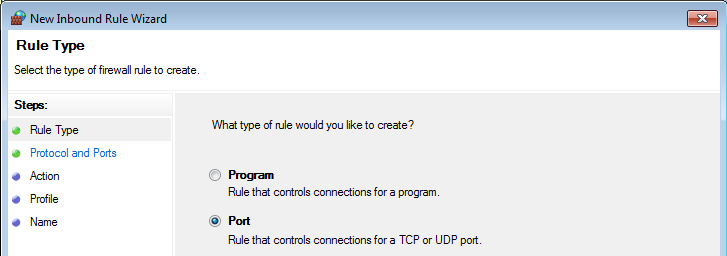
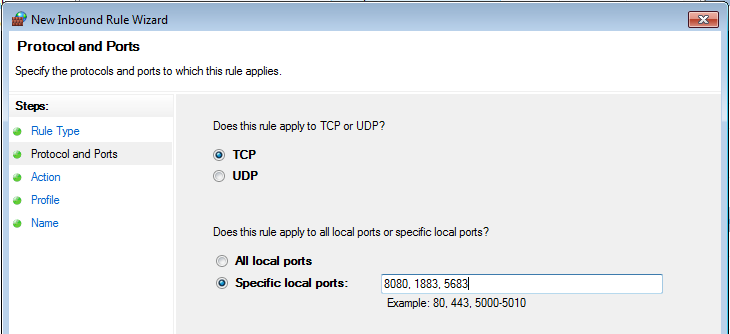
- On the “Protocol and Ports” step select “TCP” protocol and enter port list 8080, 1883, 5683 in the “Specific local ports” field:
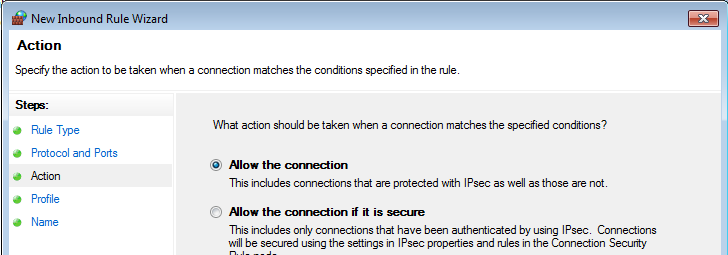
- On the “Action” step leave “Allow the connection” option selected:
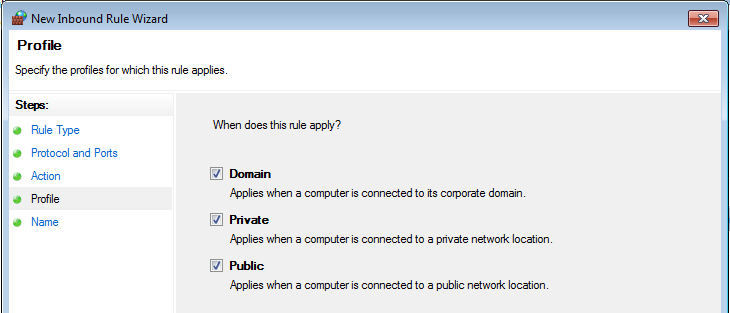
- On the “Profile” step select Windows network profiles when to apply this rule:
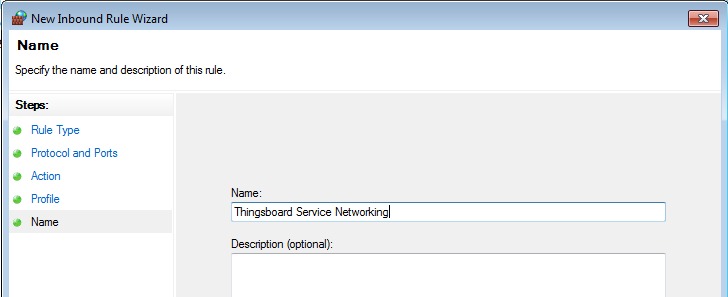
- Finally, give the name to this rule (for ex. “ThingsBoard Service Networking”) and click “Finish”.
Next steps
-
Getting started guides - These guides provide quick overview of main ThingsBoard features. Designed to be completed in 15-30 minutes.
-
Connect your device - Learn how to connect devices based on your connectivity technology or solution.
-
Data visualization - These guides contain instructions on how to configure complex ThingsBoard dashboards.
-
Data processing & actions - Learn how to use ThingsBoard Rule Engine.
-
IoT Data analytics - Learn how to use rule engine to perform basic analytics tasks.
-
Advanced features - Learn about advanced ThingsBoard features.
-
Contribution and Development - Learn about contribution and development in ThingsBoard.