- Key application areas
- Install solution template
- Dashboard
- Devices
- Level measurement representation
- Alarms
- Conclusion
The Fuel Level Monitoring solution template provides a complete, ready-to-use system for monitoring liquid levels in stationary tanks. It enables real-time visualization of fuel levels, automatic volume calculation based on tank geometry, consumption and refilling tracking, and proactive alarm management.
With a single installation action, the solution deploys a fully functional dashboard, device profiles, rule chains, alarms, and demo devices.
The template is suitable for industrial, agricultural, construction, and fleet depot scenarios where accurate fuel inventory tracking and early detection of critical conditions are required.
Key application areas
This solution template can be used as a blueprint for:
- Dashboard. The Fuel Level Monitoring dashboard provides an interactive map with color-coded tank status markers, centralized alarm management, tools for tank creation and configuration, and historical analytics for fuel consumption and refilling events.
- Devices. The solution includes four pre-provisioned tank sensor devices that are already connected and immediately provide demo telemetry data.
- Device Profiles and Processing Logic. A dedicated Tank device profile is included with preconfigured alarm rules, along with a Fuel Monitoring rule chain that handles alarm counting, sensor status calculation, and device connectivity management.
- Volume Calculation Engine. The solution includes a volume calculation engine that supports nine predefined tank shapes and automatically converts sensor height measurements into volume values, with support for both fill-height and remaining-space sensor types.
Install solution template
To understand how the Fuel level monitoring solution works, start by installing the solution template.
You will need access to ThingsBoard Professional Edition. The easiest way is to use the ThingsBoard Cloud. Alternatively, you can install ThingsBoard using the Professional Edition installation guide.
- Go to the Solution templates page.
- Find Fuel level monitoring and click Install.
- Follow the provided configuration instructions.
- Once the installation is complete, click Close.
- The Fuel level monitoring dashboard opens automatically.
After installation, a fully functional simulation for monitoring liquid levels in stationary tanks is created automatically. No devices, integrations, or custom code are required to start exploring the solution.
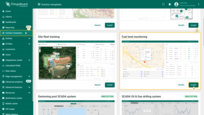
Dashboard
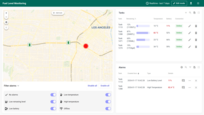
As part of this solution, we have created the dashboard. This dashboard contains 2 states that are specialised for monitoring fuel levels in tanks, observing consumption statistics, managing devices.
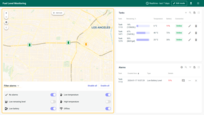
Main state:
- provides location and status of tanks through colored markers that could be filtered upon specific statuses by switchers, each color representing a different status like normal, low battery, alarm conditions, etc.
- displays a list of all tanks, allowing users to edit, delete, or add new tanks, and providing essential data such as remaining fuel percentage, temperature, battery, and connection status. Here, users can select different tanks and switch between various units of measurement to tailor the view to their specific needs.
- monitor lists all alarms related to fuel level, temperature, and battery level, and allows users to set conditions under which alarms will be triggered.
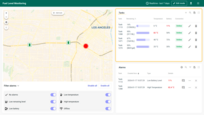
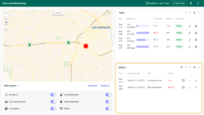
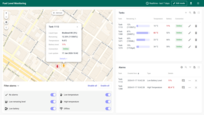
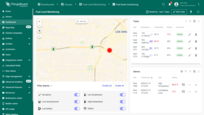
The Tank state displays the remaining fuel level for a specific tank, provides detailed tank information with editable fields and location, shows time-stamped records of consumption and replenishment, visualizes fuel level and consumption trends over time, and lists all alarms associated with the tank.
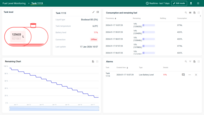
The incorporation of tanks and units selection further personalises the user interface, enabling more precise monitoring and management, while the streamlined interface ensures swift navigation and enhanced user experience, catering to various monitoring and management needs related to fuel level in tanks.
Devices
We have already created nine sensors and loaded some demo data for them. The solution expects that the sensor device will upload temperature, fuel and battery level. The most simple example of the expected payload is in JSON format:
1
{"battery": 77, "fuelLevel": 91, "fuelHeight": 125, "temperature": 32 }
You may find the exact commands to send data on behalf of created devices in the solution instructions. See connecting devices for various connectivity options to connect real devices.
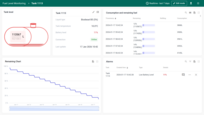
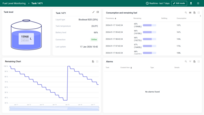
Level measurement representation
Our dashboard can calculate the volume of the presented tank shapes based on the “filling height” or “remaining space”.
- Filling Height: The dashboard calculates the volume of different tank shapes based on “filling height”, allowing for adaptable and precise level measurement representation.
- Remaining Space: Similarly, the volume can also be calculated considering the “remaining space” in the tank, factoring in additional components like the “Sensor gap”, which represents parts of the tank not included in the height calculation. This approach ensures more flexible and detailed tank volume calculation, particularly when specific parts of the tank, such as the neck, are not to be included in the volume calculation.
You can find more detailed information about calculating the volume of the presented tank shapes based on the “filling height” or “remaining space” in the solution instructions.
Alarms
Alarms are generated using four Alarm rules in the “Tank Sensor” device profile. User may configure the alarm rules via the “Fuel Level Monitoring” dashboard using “Alarm rules” form.
Conclusion
The Fuel Level Monitoring solution provides real-time visibility into fuel levels and consumption across assets. Using telemetry, calculated metrics, and alarms, it helps detect abnormal usage, prevent shortages, and optimize refueling processes. The template offers a ready-to-use foundation for reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency through centralized fuel monitoring.