During widget development, there might be instances where the default subscription functionality doesn’t suffice. In such scenarios, a custom subscription can be employed. Typically, custom subscriptions are used with static widget types, as they don’t have default subscription logic.
Main information
For creating custom subscriptions you have to use function createSubscription from Widget Subscription API:
1
widgetContext.createSubscription(options);
The object options contain comprehensive information regarding the subscription and include the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
type |
widgetType | Sets subscription type. |
datasources |
Array<Datasource> | Contains information about the data to be subscribed to. |
alarmSource |
Datasource | Contains information about the alarms to be subscribed to. |
datasourcesOptional |
Boolean | Sets whether the datasources are optional. For static widget type always true. |
hasDataPageLink |
Boolean | Sets whether pageLink is used for subscribing. |
singleEntity |
Boolean | Determines if data will be retrieved only from the first found entity. |
pageSize |
Number | Determines the number of entities displayed on a page. |
warnOnPageDataOverflow |
Boolean | Activates warning about overflow page data. |
useDashboardTimewindow |
Boolean | If active, the subscription will be used time window from dashboardTimewindow, otherwise will be used timeWindowConfig (using to change time window in time-series subscriptions). |
dashboardTimewindow |
Timewindow | Contains the dashboard timewindow. |
timeWindowConfig |
Timewindow | Sets the custom timewindow. |
legendConfig |
LegendConfig | Sets params of legend. |
decimals |
Number | Sets number of digits after floating point for all keys. |
units |
String | Sets special symbol to show next to value for all keys. |
callbacks |
WidgetSubscriptionCallbacks | The set of callbacks used in the subscription life cycle. |
Datasources
The Datasources object describes what data you want to subscribe to. The main functions are:
- Description of the keys that you want to subscribe to.
- Specifying the entities you need to extract data from.
- Filtering entities based on specific keys and values.
The datasource object includes the subsequent fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
type |
DatasourceType/any | Sets type of datasource. |
aliasName |
String | Name of datasource. |
dataKeys |
Array<DataKey> | Describes the keys to be subscribed to. |
latestDataKeys |
Array<DataKey> | Use this in case you have time-series subscription and at the same time, you want to subscribe to the latest data for some keys. |
pageLink |
EntityDataPageLink | Sets pageLink for datasource. |
keyFilters |
Array<KeyFilter> | Filters the data to be subscribed to by the value of the keys. You can find all information about key filters here. |
entityFilter |
EntityFilter | Filters the data to be subscribed to by entities params. You can find all information about entity filters here. |
Callbacks
Callbacks object has a set of functions that are called at different stages of the subscription life cycle. It has the following fields:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
onDataUpdated |
Called after updating data. |
onLatestDataUpdated |
Called only in time-series subscription after updating data from latestDataKeys. |
onDataUpdateError |
Called after an error in updating data. |
onLatestDataUpdateError |
Called only in time-series subscription after error in updating data from latestDataKeys. |
legendDataUpdated |
Called after updating legend data. |
timeWindowUpdated |
Called after updating timewindow. |
dataLoading |
Called after loading data. |
rpcStateChanged |
Called after changing RPC state. |
onRpcSuccess |
Called exclusively in the RPC subscription after a successful RPC. |
onRpcFailed |
Called exclusively in the RPC subscription after a failed RPC. |
Entity Filters
The entity filter is an important part of creating custom subscriptions as it defines the entities from which your subscription extracts information. The Entity Filter body depends on the type parameter. Let’s delve into the available entity filter types, which, in essence, align with the existing dashboard aliases.
- Single Entity
Allows to filter only one entity based on the id. For example, this entity filter selects certain device:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
{
type: "singleEntity",
singleEntity: {
id: "d521edb0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092",
entityType: "DEVICE"
}
}
- Group Entities Filter
Allows to filter multiple entities of the same type using the entity group type and id. For example, this entity filter selects all devices that belong to the group e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092:
1
2
3
4
5
{
type: "entityGroup",
groupType: "DEVICE",
entityGroup: "e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092"
}
- Entity List Filter
Allows to filter entities of the same type using their ids. For example, this entity filter selects two devices:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
{
type: "entityList",
entityType: "DEVICE",
entityList: [
"e6501f30-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092",
"e6657bf0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092"
]
}
- Entity Name Filter
Allows to filter entities of the same type using the starts with expression on entity name. For example, this entity filter selects all devices with names starting with Air Quality:
1
2
3
4
5
{
type: "entityName",
entityType: "DEVICE",
entityNameFilter: "Air Quality"
}
- Entity Type Filter
Allows to filter entities based on their type (CUSTOMER, USER, DASHBOARD, ASSET, DEVICE, etc). For example, this entity filter selects all tenant customers:
1
2
3
4
{
type: "entityType",
entityType: "CUSTOMER"
}
- Group List Filter
Return multiple groups of the same type using specified ids. For example, this entity filter selects 2 device groups (if they are present in the system) with ids e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092 and e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54093:
1
2
3
4
5
{
type: "entityGroupList",
groupType: "DEVICE",
entityGroupList: ["e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092", "e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54093"]
}
- Group Name Filter
Allows to filter entity groups based on their type and the starts with expression on their name. For example, this entity filter selects all devices with names starting with CAT:
1
2
3
4
5
{
type: "entityGroupName",
groupType: "DEVICE",
entityGroupNameFilter: "CAT"
}
- Entities by Group Name Filter
Allows to filter entities that belong to group based on the entity type and the group name. Optional parameter ownerId allows you to specify the owner of the group (Tenant or Customer, current user owner by default). For example, this entity filter selects all devices that belong to Water Meters group:
1
2
3
4
5
{
type: "entitiesByGroupName",
groupType: "DEVICE",
entityGroupNameFilter: "Water Meters"
}
Another example, this entity filter selects all devices that belong to Water Meters group which in turn belongs to (sub-)Customer with id e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54093:
1
2
3
4
5
6
{
type: "entitiesByGroupName",
ownerId: "e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54093",
groupType: "DEVICE",
entityGroupNameFilter: "Water Meters"
}
- Entity owner Filter
Allows to fetch owner (Tenant or Customer) of the specified entity. For example, this entity filter selects owner of the device with id e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54093:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
{
type: "stateEntityOwner",
singleEntity: {
id: "d521edb0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092",
entityType: "DEVICE"
}
}
- Asset Type Filter
Allows to filter assets based on their type and the ‘starts with’ expression over their name. For example, this entity filter selects all ‘charging station’ assets with name that start with ‘Tesla’:
1
2
3
4
5
6
{
type: "assetType",
assetTypes: ["charging station"],
assetNameFilter: "Tesla"
}
- Device Type Filter
Allows to filter devices based on their type and the ‘starts with’ expression over their name. For example, this entity filter selects all ‘Temperature Sensor’ devices with name that start with ‘ABC’:
1
2
3
4
5
6
{
type: "deviceType",
deviceTypes: ["Temperature Sensor"],
deviceNameFilter: "ABC"
}
- Entity View Filter
Allows to filter entity views based on their type and the ‘starts with’ expression over their name. For example, this entity filter selects all ‘Concrete Mixer’ entity views with name that start with ‘CAT’:
1
2
3
4
5
6
{
type: "entityViewType",
entityViewTypes: ["Concrete Mixer"],
entityViewNameFilter: "CAT"
}
- Edge Type Filter
Allows to filter edge instances based on their type and the ‘starts with’ expression over their name. For example, this entity filter selects all ‘Factory’ edge instances with name that start with ‘Nevada’:
1
2
3
4
5
6
{
type: "edgeType",
edgeTypes: ["Factory"],
edgeNameFilter: "Nevada"
}
- Api Usage Filter
Allows to query for Api Usage based on optional customer id. If the customer id is not set, returns current tenant API usage. For example, this entity filter selects the Api Usage entity for customer with id e6501f30-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
{
type: "apiUsageState",
customerId: {
id: "d521edb0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092",
entityType: "CUSTOMER"
}
}
- Relations Query Filter
Allows to filter entities that are related to the provided root entity. Possible direction values are TO and FROM. The maxLevel defines how many relation levels should the query search recursively. Assuming the maxLevel > 1, the fetchLastLevelOnly defines either to return all related entities or only entities that are on the last level of relations. The filter objects(inside filters array) allows you to define the relation type and set of acceptable entity types to search for. The relation query calculates all related entities, even if they are filtered using different relation types, and then extracts only those that match the filters.
For example, this entity filter selects all devices and assets that are related to the asset with id e51de0c0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
{
type: "relationsQuery",
rootEntity: {
entityType: "ASSET",
id: "e51de0c0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092"
},
direction: "FROM",
maxLevel: 1,
fetchLastLevelOnly: false,
filters: [
{
relationType: "Contains",
entityTypes: [
"DEVICE",
"ASSET"
]
}
]
}
- Asset Search Query
Allows to filter assets that are related to the provided root entity. Filters related assets based on the relation type and set of asset types. Possible direction values are TO and FROM. The maxLevel defines how many relation levels should the query search recursively. Assuming the maxLevel > 1, the fetchLastLevelOnly defines either to return all related entities or only entities that are on the last level of relations. The relationType defines the type of the relation to search for. The assetTypes defines the type of the asset to search for. The relation query calculates all related entities, even if they are filtered using different relation types, and then extracts only assets that match relationType and assetTypes conditions.
For example, this entity filter selects Charging station assets that are related to the asset with id e51de0c0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092 using Contains relation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
{
type: "assetSearchQuery",
rootEntity: {
entityType: "ASSET",
id: "e51de0c0-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092"
},
direction: "FROM",
maxLevel: 1,
fetchLastLevelOnly: false,
relationType: "Contains",
assetTypes: [
"Charging station"
]
}
- Device Search Query
Allows to filter devices that are related to the provided root entity. Filters related devices based on the relation type and set of device types. Possible direction values are TO and FROM. The maxLevel defines how many relation levels should the query search recursively. Assuming the maxLevel > 1, the fetchLastLevelOnly defines either to return all related entities or only entities that are on the last level of relations. The relationType defines the type of the relation to search for. The deviceTypes defines the type of the device to search for. The relation query calculates all related entities, even if they are filtered using different relation types, and then extracts only devices that match relationType and deviceTypes conditions.
For example, this entity filter selects Charging port and Air Quality Sensor devices that are related to the asset with id e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092 using Contains relation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
{
type: "deviceSearchQuery",
rootEntity: {
entityType: "ASSET",
id: "e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092"
},
direction: "FROM",
maxLevel: 2,
fetchLastLevelOnly: true,
relationType: "Contains",
deviceTypes: [
"Air Quality Sensor",
"Charging port"
]
}
- Entity View Query
Allows to filter entity views that are related to the provided root entity. Filters related entity views based on the relation type and set of entity view types. Possible direction values are TO and FROM. The maxLevel defines how many relation levels should the query search recursively. Assuming the maxLevel > 1, the fetchLastLevelOnly defines either to return all related entities or only entities that are on the last level of relations. The relationType defines the type of the relation to search for. The entityViewTypes defines the type of the entity view to search for. The relation query calculates all related entities, even if they are filtered using different relation types, and then extracts only devices that match relationType and deviceTypes conditions.
For example, this entity filter selects Concrete mixer entity views that are related to the asset with id e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092 using Contains relation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
{
type: "entityViewSearchQuery",
rootEntity: {
entityType: "ASSET",
id: "e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092"
},
direction: "FROM",
maxLevel: 1,
fetchLastLevelOnly: false,
relationType: "Contains",
entityViewTypes: [
"Concrete mixer"
]
}
- Edge Search Query
Allows to filter edge instances that are related to the provided root entity. Filters related edge instances based on the relation type and set of edge types. Possible direction values are TO and FROM. The maxLevel defines how many relation levels should the query search recursively. Assuming the maxLevel > 1, the fetchLastLevelOnly defines either to return all related entities or only entities that are on the last level of relations. The relationType defines the type of the relation to search for. The edgeTypes defines the type of the edge to search for. The relation query calculates all related entities, even if they are filtered using different relation types, and then extracts only edge instances that match relationType and edgeTypes conditions.
For example, this entity filter selects Factory edge instances that are related to the asset with id e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092 using Contains relation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
{
type: "edgeSearchQuery",
rootEntity: {
entityType: "ASSET",
id: "e52b0020-2a7a-11ec-94eb-213c95f54092"
},
direction: "FROM",
maxLevel: 2,
fetchLastLevelOnly: true,
relationType: "Contains",
edgeTypes: [
"Factory"
]
}
- Scheduler Event Query
Allows to filter schedulers based on entity and scheduler event type. For example, this entity filter selects all schedulers with event type Light switch scheduler and related to the device with id e01d2630-d710-11ef-a015-9bbc9baea46f.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
{
type: "schedulerEvent",
originator: {
entityType: "DEVICE",
id: "e01d2630-d710-11ef-a015-9bbc9baea46f"
},
eventType: "Light switch scheduler"
}
Key Filters
Key Filter allows you to define complex logical expressions over entity field, attribute, or latest time series value. The filter is defined using key, valueType, and predicate objects. The Single Entity Query may have zero, one, or multiple predicates. If multiple filters are defined, they are evaluated using logical AND. The example below checks that temperature of the entity is above 20 degrees:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
{
key: {
type: "TIME_SERIES",
key: "temperature"
},
valueType: "NUMERIC",
predicate: {
operation: "GREATER",
value: {
defaultValue: 20,
dynamicValue: null
},
type: "NUMERIC"
}
}
Now let’s review key, valueType and predicate objects in detail.
- Key object
Filter Key defines either entity field, attribute, or telemetry. It is a JSON object that consists of the key name and type. The following filter key types are supported:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
CLIENT_ATTRIBUTE |
Used for client attributes. |
SHARED_ATTRIBUTE |
Used for shared attributes. |
SERVER_ATTRIBUTE |
Used for server attributes. |
ATTRIBUTE |
Used for any of the above. |
TIME_SERIES |
Used for time-series values. |
ENTITY_FIELD |
Used for accessing entity fields like name, label, etc. The list of available fields depends on the entity type. |
ALARM_FIELD |
Similar to entity field, but is used in alarm queries only. |
Object example:
1
2
3
4
{
type: "SERVER_ATTRIBUTE",
key: "maxTemperature"
}
- Value Type
Provides a hint about the data type of the entity field that is defined in the filter key. The value type impacts the list of possible operations that you may use in the corresponding predicate. For example, you may use STARTS_WITH or END_WITH, but you can’t use GREATER_OR_EQUAL for string values. The following filter value types and corresponding predicate operations are supported:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
STRING |
Used to filter any String or JSON values. Operations: EQUAL, NOT_EQUAL, STARTS_WITH, ENDS_WITH, CONTAINS, NOT_CONTAINS. |
NUMERIC |
Used for Long and Double values. Operations: EQUAL, NOT_EQUAL, GREATER, LESS, GREATER_OR_EQUAL, LESS_OR_EQUAL. |
BOOLEAN |
Used for Boolean values. Operations: EQUAL, NOT_EQUAL. |
DATE_TIME |
Similar to numeric, transforms value to milliseconds since epoch. Operations: EQUAL, NOT_EQUAL, GREATER, LESS, GREATER_OR_EQUAL, LESS_OR_EQUAL. |
- Predicate object
Filter Predicate defines the logical expression to evaluate. The list of available operations depends on the filter value type, see above. The platform supports 4 predicate types: STRING, NUMERIC, BOOLEAN, and COMPLEX. The last one allows combining multiple operations over one filter key.
Simple predicate example to check value < 100:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
{
operation: "LESS",
value: {
defaultValue: 100,
dynamicValue: null
},
type: "NUMERIC"
}
Complex predicate example, to check value < 10 or value > 20:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
{
type: "COMPLEX",
operation: "OR",
predicates: [
{
operation: "LESS",
value: {
defaultValue: 10,
dynamicValue: null
},
type: "NUMERIC"
},
{
operation: "GREATER",
value: {
defaultValue: 20,
dynamicValue: null
},
type: "NUMERIC"
}
]
}
More complex predicate example, to check value < 10 or (value > 50 && value < 60):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
{
type: "COMPLEX",
operation: "OR",
predicates: [
{
operation: "LESS",
value: {
defaultValue: 10,
dynamicValue: null
},
type: "NUMERIC"
},
{
type: "COMPLEX",
operation: "AND",
predicates: [
{
operation: "GREATER",
value: {
defaultValue: 50,
dynamicValue: null
},
type: "NUMERIC"
},
{
operation: "LESS",
value: {
defaultValue: 60,
dynamicValue: null
},
type: "NUMERIC"
}
]
}
]
}
You may also want to replace hardcoded values (for example, temperature > 20) with the more a dynamic expression (for example, temperature > value of the tenant attribute with key temperatureThreshold). It is possible to use dynamicValue to define attribute of the tenant, customer or user that is performing the API call. See example below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
{
operation: "GREATER",
value: {
defaultValue: 0,
dynamicValue: {
sourceType: "CURRENT_USER",
sourceAttribute: "temperatureThreshold"
}
},
type: "NUMERIC"
}
Note that you may use CURRENT_USER, CURRENT_CUSTOMER and CURRENT_TENANT as a sourceType. The defaultValue is used when the attribute with such a name is not defined for the chosen source.
Available for users with TENANT_ADMIN or CUSTOMER_USER authority.
Examples
Below is a set of typical custom subscription examples.
Subscription for counting
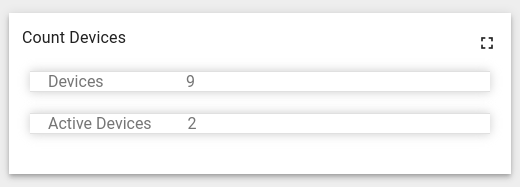
Let’s create a custom subscription for the number of devices in the system, and the number of active devices:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
...
self.onInit = function() {
...
const datasources = [
{
type: "entityCount", //Sets that there is a subscription to the entity count
dataKeys: [
{
decimals: 0, //Number of digits after floating point for this key
label: "Devices", //Key label
name: "count", //Key name
settings: {},
type: "count" //Key type
}
],
entityFilter: //Describes entities (See Entity Filters topic)
{
type: "entityType", //Entity filter type
entityType: "DEVICE" //Entity type
}
},
{
type: "entityCount",
dataKeys: [
{
decimals: 0,
label: "Active Devices",
name: "count",
settings: {},
type: "count"
}
],
entityFilter: //Describes entities (See Entity Filters topic)
{
type: "entityType",
entityType: "DEVICE"
},
keyFilters: //Filtering entity by keys (See Key Filters topic)
[
{
key: {
key: "active", //Key name
type: "ATTRIBUTE" //Key type
},
predicate: {
operation: "EQUAL", //Operation type (You can find full list of operations in Key Filters topic)
type: "BOOLEAN", //Predicate value type
value: {
defaultValue: true //Predicate value
}
},
valueType: "BOOLEAN" //Value type
}
]
}
];
const subscriptionOptions = {
type: 'latest', //Subscription type
datasources: datasources, //Describes what data you want to subscribe
callbacks: //Sets callbacks for subscription
{
onDataUpdated: () => {
//Data ready to processing
self.onDataUpdated();
}
}
};
self.ctx.subscriptionApi.createSubscription(subscriptionOptions, true).subscribe(
(subscription) => {
//Data is not available here! Code below just indicates where data will save.
self.ctx.defaultSubscription = subscription; //Saves subscription information into widget context
self.ctx.data = subscription.data; //Saves data into widget context
self.ctx.datasources = subscription.datasources; //Saves datasource into widget context
...
}
);
...
}
self.onDataUpdated = function() {
//Data processing logic should be place here
}
...
As a result, a subscription will be created to count devices in the system and count active devices (the widget is illustrative):
Subscription for attributes/telemetry
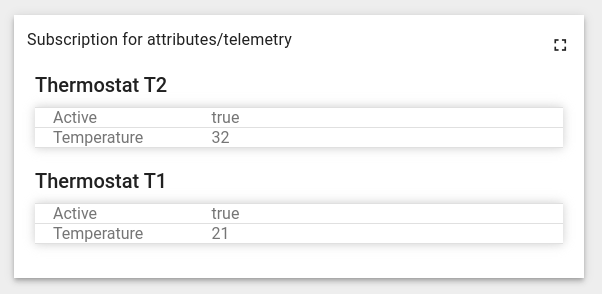
Let’s create a custom subscription to the latest temperature key value for active devices:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
...
self.onInit = function() {
...
const datasources = [
{
type: "entity", //Indicates that there is a subscription to entity data
dataKeys: //Describes keys
[
{
decimals: 0, //Number of digits after floating point for this key
label: "Temperature", //Key label
name: "temperature", //Key name
settings: {},
type: "timeseries" //Key type
},
{
decimals: 0,
label: "Active",
name: "active",
settings: {},
type: "attribute"
}
],
entityFilter: //Describes entities (See Entity Filters topic)
{
type: "entityType", //Entity filter type
entityType: "DEVICE" //Entity type
},
keyFilters: //Filtering entity by keys (See Key Filters topic)
[
{
key: {
key: "active", //Key name
type: "ATTRIBUTE" //Key type
},
predicate: {
operation: "EQUAL", //Operation type (You can find full list of operations in Key Filters topic)
type: "BOOLEAN", //Predicate value type
value: {
defaultValue: true //Predicate value
}
},
valueType: "BOOLEAN" //Value type
}
]
}
];
const subscriptionOptions = {
type: 'latest', //Subscription type
datasources: datasources, //Describes what data you want to subscribe
callbacks: //Sets callbacks for subscription
{
onDataUpdated: () => {
//Data ready to processing
self.onDataUpdated();
}
}
};
self.ctx.subscriptionApi.createSubscription(subscriptionOptions, true).subscribe(
(subscription) => {
//Data is not available here! Code below just indicates where data will save.
self.ctx.defaultSubscription = subscription; //Saves subscription information into widget context
self.ctx.data = subscription.data; //Saves data into widget context
self.ctx.datasources = subscription.datasources; //Saves datasource into widget context
...
}
);
...
}
self.onDataUpdated = function() {
//Data processing logic should be place here
}
...
As a result a subscription to the temperature and active keys will be created only for active devices (the widget is illustrative):
Subscription with PageLink
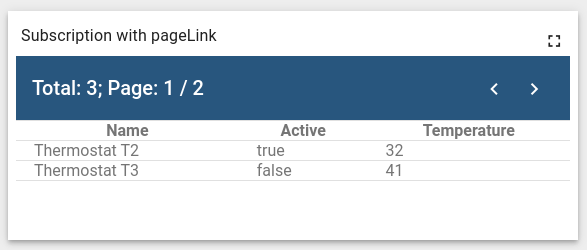
Let’s create a custom subscription to the latest temperature key value that is greater than 30 with two entities on the page:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
...
self.onInit = function() {
...
const datasources = [
{
type: "entity", //Indicates that there is a subscription to entity data
dataKeys: //Describes keys
[
{
label: "Temperature", //Key label
name: "temperature", //Key name
settings: {},
type: "timeseries" //Key type
},
{
label: "Active",
name: "active",
settings: {},
type: "attribute"
}
],
entityFilter: //Describes entities (See Entity Filters topic)
{
type: "deviceType", //Entity filter type
deviceTypes: [
"thermostat" //Device type
]
},
keyFilters: //Filtering entity by keys (See Key Filter topic)
[
{
key: {
key: "temperature", //Key name
type: "TIME_SERIES" //Key type
},
predicate: {
operation: "GREATER", //Operation type (You can find full list of operations in Key Filters topic)
type: "NUMERIC", //Predicate value type
value: {
defaultValue: 30 //Predicate value
}
},
valueType: "NUMERIC" //Value type
}
]
}
];
const subscriptionOptions = {
type: 'latest', //Subscription type
datasources: datasources, //Describes what data you want to subscribe
hasDataPageLink: true, //Sets subscription into pageLink mode
callbacks: //Sets callbacks for subscription
{
onDataUpdated: () => {
//Data ready to processing
self.onDataUpdated();
}
}
};
self.ctx.$scope.pageLink = {
page: 0, //Page Number
pageSize: 2, //Number of entities per page
dynamic: true //If true, new entities will be automatically added to the widget if they meet the given parameters
};
self.ctx.subscriptionApi.createSubscription(subscriptionOptions, true).subscribe(
(subscription) => {
//Data is not available here! Code below just indicates where data will save.
self.ctx.defaultSubscription = subscription; //Saves subscription information into widget context
subscribeForPaginatedData(self.ctx.$scope.pageLink);
self.ctx.data = subscription.data; //Saves data into widget context
self.ctx.datasources = subscription.datasources; //Saves datasource into widget context
self.ctx.dataPages = subscription.dataPages; //Saves dataPages into widget context
self.ctx.datasourcePages = subscription.datasourcePages; //Saves datasourcePages into widget context
...
}
);
...
}
self.onDataUpdated = function() {
//Data processing logic should be place here
}
function subscribeForPaginatedData(pageLink) {
self.ctx.defaultSubscription.subscribeAllForPaginatedData(pageLink, null); //Get information by pageLink params
}
...
As a result, a subscription to the temperature and active keys will be created using PageLink (the widget is illustrative):
Subscription for telemetry time series
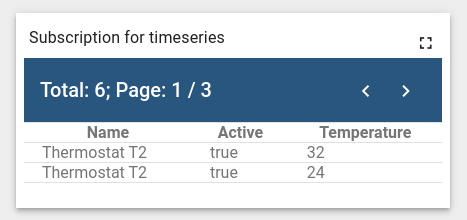
Let’s create a custom subscription to the time-series of temperature key from Thermostat T2 device:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
...
self.onInit = function() {
...
const datasources = [
{
type: "entity", //Indicates that there is a subscription to entity data
dataKeys: //Describes time-series keys
[
{
label: "Temperature", //Key label
name: "temperature", //Key name
settings: {},
type: "timeseries" //Key type
}
],
latestDataKeys: //Describes latest keys
[
{
label: "Active", //Key label
name: "active", //Key name
settings: {},
type: "attribute" //Key type
}
],
entityFilter: //Describes entities (See Entity Filters topic)
{
type: "entityName", //Entity filter type
entityType: "DEVICE", //Entity type
entityNameFilter: "Thermostat T2" //Entity name
}
}
];
const subscriptionOptions = {
type: 'timeseries', //Subscription type
datasources: datasources, //Describes what data you want to subscribe
ignoreDataUpdateOnIntervalTick: true, //if true onDataUpdated will be triggered only when new data appears otherwise onDataUpdate will be triggered every second
useDashboardTimewindow: true,
callbacks: //Sets callbacks for subscription
{
onDataUpdated: () => {
//Data ready to processing
self.onDataUpdated();
}
}
};
self.ctx.subscriptionApi.createSubscription(subscriptionOptions, true).subscribe(
(subscription) => {
//Data is not available here! Code below just indicates where data will save.
self.ctx.defaultSubscription = subscription; //Saves subscription information into widget context
self.ctx.data = subscription.data; //Saves data into widget context
self.ctx.datasources = subscription.datasources; //Saves datasource into widget context
self.ctx.dataPages = subscription.dataPages; //Saves dataPages into widget context
self.ctx.datasourcePages = subscription.datasourcePages; //Saves datasourcePages into widget context
...
}
);
...
}
self.onDataUpdated = function() {
//Data processing logic should be place here
}
...
As a result, a subscription to the temperature telemetry time-series will be created (the widget is illustrative):
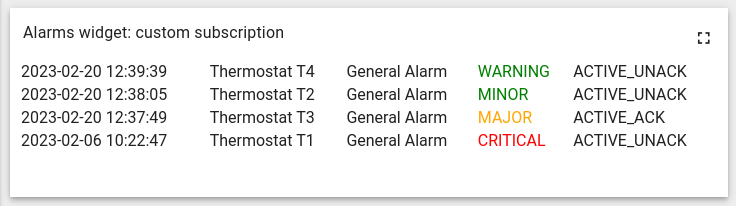
Subscription for alarms
Let’s create a custom subscription to the alarms from thermostat type devices
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
...
self.onInit = function() {
...
const alarmSource = {
type: 'entity', //Indicates that there is a subscription to entity data
dataKeys: //Describes keys
[
{
type: "alarm", //Key type
name: "createdTime" //Key name
},
{
type: "alarm",
name: "originator"
},
{
type: "alarm",
name: "type"
},
{
type: "alarm",
name: "severity"
},
{
type: "alarm",
name: "status"
}
],
entityFilter: //Describes entities (See Entity Filters topic)
{
type: "deviceType", //Entity filter type
deviceTypes: [
"thermostat" //Device type
]
}
};
const alarmDataPageLink = {
page: 0, //Page Number
pageSize: 10, //Number of alarms per page
statusList: [], //Status list (all statuses if empty)
severityList: [], //Severity list (all severities if empty)
typeList: [], //Type list (all alarm types if empty)
sortOrder: //Sorting params
{
key: {
key: "createdTime", //Key name
type: "ALARM_FIELD" //Key type
},
direction: "DESC"
}
};
const subscriptionOptions = {
type: 'alarm', //Subscription type
alarmSource: alarmSource, //Describes what alarms data you want to subscribe
useDashboardTimewindow: true,
callbacks: //Sets callbacks for subscription
{
onDataUpdated: () => {
//Data ready to processing
self.onDataUpdated();
}
}
};
self.ctx.subscriptionApi.createSubscription(subscriptionOptions, true).subscribe(
(subscription) => {
//Data is not available here! Code below just indicates where data will save.
self.ctx.alarmsSubscription = subscription; //Saves subscription information into widget context
self.ctx.alarmsSubscription.subscribeForAlarms(alarmDataPageLink, null); //Get information by pageLink params
...
}
);
...
}
self.onDataUpdated = function() {
//Data processing logic should be place here
}
...
As a result, a subscription to the thermostat’s alarms will be created (the widget is illustrative):
Subscription with post-processing
Custom subscription supports the ability to post-process incoming data. Next example will be based on Subscription for attributes/telemetry
Sometimes there is a need to provide the user with the ability to modify the incoming data. Imagine the following situation: a device sends weight telemetry in kilograms, but we also want to give the user the ability to convert this value. In this case, we could use the post-processing feature.
First of all, we need to create a custom setting schema that will contain user’s function that will convert weight telemetry. We will use a simple schema that contains JavaScript field:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
{
"schema":{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"weightPostProcessingFunction": {
"title": "Weight post-processing: f(time, value, prevValue, timePrev, prevOrigValue)",
"type": "string",
"default": "return value;"
}
}
},
"form": [
{
"key": "weightPostProcessingFunction",
"type": "javascript"
}
]
}
Now let’s create a custom subscription. For clarity, we will add two fields: one contains the original value and the second one contains the processed value:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
...
self.onInit = function() {
...
const datasources = [
{
type: "entity", //Indicates that there is a subscription to entity data
dataKeys: //Describes keys
[
{
decimals: 0, //Number of digits after floating point for this key
label: "Weight telemetry", //Key label
name: "weight", //Key name
settings: {},
type: "timeseries" //Key type
},
{
decimals: 0, //Number of digits after floating point for this key
label: "Post processing weight", //Key label
name: "weight", //Key name
settings: {},
usePostProcessing: true, //Enable post-processing
postFuncBody: self.ctx.settings.postProcessingFunction, //Set post-processing function from widget settings
type: "timeseries" //Key type
},
{
decimals: 0,
label: "Active",
name: "active",
settings: {},
type: "attribute"
}
],
entityFilter: //Describes entities (See Entity Filters topic)
{
type: "entityType", //Entity filter type
entityType: "DEVICE" //Entity type
},
keyFilters: //Filtering entity by keys (See Key Filters topic)
[
{
key: {
key: "active", //Key name
type: "ATTRIBUTE" //Key type
},
predicate: {
operation: "EQUAL", //Operation type (You can find full list of operations in Key Filters topic)
type: "BOOLEAN", //Predicate value type
value: {
defaultValue: true //Predicate value
}
},
valueType: "BOOLEAN" //Value type
}
]
}
];
const subscriptionOptions = {
type: 'latest', //Subscription type
datasources: datasources, //Describes what data you want to subscribe to
callbacks: //Sets callbacks for subscription
{
onDataUpdated: () => {
//Data ready to processing
self.onDataUpdated();
}
}
};
self.ctx.subscriptionApi.createSubscription(subscriptionOptions, true).subscribe(
(subscription) => {
//Data is not available here! Code below just indicates where data will save.
self.ctx.defaultSubscription = subscription; //Saves subscription information into widget context
self.ctx.data = subscription.data; //Saves data into widget context
self.ctx.datasources = subscription.datasources; //Saves datasource into widget context
...
}
);
}
self.onDataUpdated = function() {
//Data processing logic should be place here
}
...
The subscription is ready now let’s convert weight telemetry from kilograms into grams:
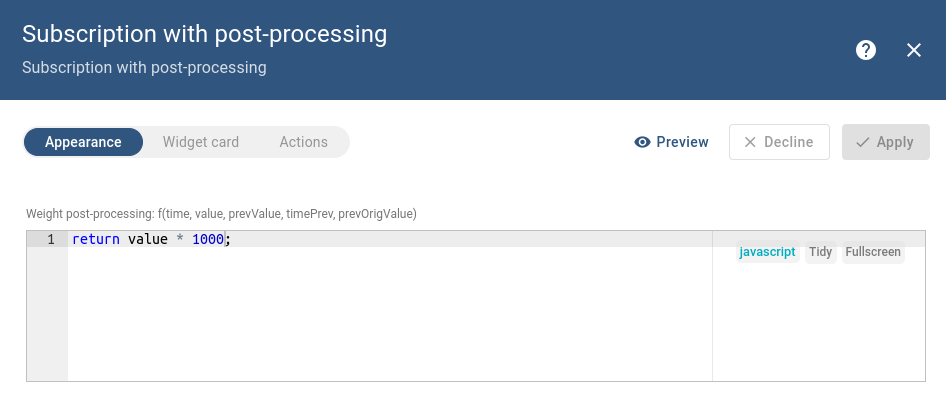

As you can see, despite subscribing to the same key twice, the output shows different values because one of them was additionally transformed using the post-processing function.