This guide provides an overview of the various options you have to manage authentication and authorization for MQTT clients in accordance with your specific requirements and infrastructure.
Authentication refers to the process of verifying the identity of MQTT clients connecting to the broker. It ensures that only authenticated clients can access the system. The guide will explore different authentication mechanisms such as basic authentication, and SSL/TLS client certificate authentication. It will explain how to configure and enable these authentication methods based on your security needs.
Authorization, on the other hand, involves granting or denying access to specific resources or actions based on the authenticated client’s privileges. You will learn how to assign topic authorization rules to clients to control their permissions and restrict their actions within the MQTT system.
By understanding and implementing the authentication and authorization options outlined in this guide, you can ensure secure and controlled access to the MQTT broker, protecting your infrastructure and data from unauthorized access or misuse.
MQTT Listeners
TBMQ provides the flexibility to configure its listening capabilities for both the TCP and SSL/TLS protocols as well as for MQTT over WebSockets.
TCP Listener
By default, TBMQ has the TCP listener enabled on port 1883.
However, if you wish to disable the TCP listener, you can set the LISTENER_TCP_ENABLED environment variable to false.
Furthermore, if you need to change the host address that the broker is binding to or the port it is listening on,
you can modify the LISTENER_TCP_BIND_ADDRESS and LISTENER_TCP_BIND_PORT variables, respectively.
This gives you the flexibility to configure the broker to listen on a specific network interface and port of your choice.
By adjusting these environment variables, you can customize the TCP listening behavior of TBMQ to suit your specific requirements.
TLS Listener
To enable the SSL/TLS listener, set the LISTENER_SSL_ENABLED environment variable to true. By default, the broker is listening on the 8883 port.
To change the host and/or port that the broker is listening to, update the LISTENER_SSL_BIND_ADDRESS and LISTENER_SSL_BIND_PORT variables, respectively.
Choose the type of credentials you want to use by setting the LISTENER_SSL_CREDENTIALS_TYPE parameter. Currently, the supported options are PEM and KEYSTORE.
Note that you can find a list of all available properties in the configuration documentation.
If you choose KeyStore as the credentials type, you need to configure the following:
- Set
LISTENER_SSL_KEY_STOREvariable to the path to your.jksfile with the server certificate chain. - Set
LISTENER_SSL_KEY_STORE_PASSWORDvariable to the password used to access the key store. - Set
LISTENER_SSL_KEY_PASSWORDvariable to the password for the server certificate.
If you choose Pem as the credentials type, you need to configure the following:
- Set
LISTENER_SSL_PEM_CERTvariable to the path of your server certificate file. - Set
LISTENER_SSL_PEM_KEYvariable to the path of your server certificate private key file. - Set
LISTENER_SSL_PEM_KEY_PASSWORDvariable to the password of your server certificate private key.
If you require two-way TLS, you also need to configure the TrustStore by adding the trusted certificates/chains to the configured KeyStore/PEM files. For more information about configuration possibilities and certificate generation, please review the following ThingsBoard security pages.
WS Listener
By default, TBMQ has the WebSocket listener enabled on port 8084.
However, in case you want to disable the WS listener, you can set the LISTENER_WS_ENABLED environment variable to false.
Additionally, if you need to change the host address that the broker is binding to or the port it is listening on,
you can modify the LISTENER_WS_BIND_ADDRESS and LISTENER_WS_BIND_PORT variables, respectively.
WS listener is configured to negotiate via all MQTT versions by default, i.e. WS_NETTY_SUB_PROTOCOLS is set to mqttv3.1,mqtt.
The subprotocol setting mqtt represents MQTT 3.1.1 and MQTT 5.
WSS Listener
To enable the WebSocket Secure listener, set the LISTENER_WSS_ENABLED environment variable to true. By default, the broker is listening on the 8085 port.
To change the host and/or port that the broker is listening to, update the LISTENER_WSS_BIND_ADDRESS and LISTENER_WSS_BIND_PORT variables, respectively.
Choose the type of credentials you want to use by setting the LISTENER_WSS_CREDENTIALS_TYPE parameter.
Supported options are the same as for TLS listener.
If you choose KeyStore as the credentials type, you need to configure the following:
- Set
LISTENER_WSS_KEY_STOREvariable to the path to your.jksfile with the server certificate chain. - Set
LISTENER_WSS_KEY_STORE_PASSWORDvariable to the password used to access the key store. - Set
LISTENER_WSS_KEY_PASSWORDvariable to the password for the server certificate.
If you choose Pem as the credentials type, you need to configure the following:
- Set
LISTENER_WSS_PEM_CERTvariable to the path of your server certificate file. - Set
LISTENER_WSS_PEM_KEYvariable to the path of your server certificate private key file. - Set
LISTENER_WSS_PEM_KEY_PASSWORDvariable to the password of your server certificate private key.
Do not forget to configure the TrustStore by adding the trusted certificates/chains if you require two-way TLS.
WSS listener is set to the same negotiation subprotocols as WS listener. If you need to change this default behavior, update WSS_NETTY_SUB_PROTOCOLS parameter appropriately.
Authentication
TBMQ offers two authentication methods: Basic and TLS. If neither method is enabled, clients can connect to the broker and publish/subscribe to topics without any restrictions. Note: all the clients will be connected as Device client type. Creating Application clients will not be possible.
Basic Authentication
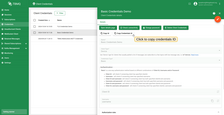
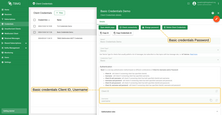
To enable basic authentication based on a username, password, and clientId in your system, follow these steps:
- Set the
SECURITY_MQTT_BASIC_ENABLEDenvironment variable totrue. - Create MQTT client credentials of type
Basicusing either the Web UI guide or the REST API guide. - Once the credentials are created, the
credentialsIdfield is auto-generated. See below for more information.
Credentials Matching
The following are the possible combinations of Basic credentials matchers:
- clientId - checks if the connecting client has specified clientId.
- username - checks if the connecting client has specified a username.
- clientId and username - checks if the connecting client has specified both clientId and username.
- username and password - checks if the connecting client has specified both username and password.
- clientId and password - checks if the connecting client has specified both clientId and password.
- clientId, username and password - checks if the connecting client has specified clientId, username, and password.
Credentials ID
When a client connects, the combination of the username, password, and clientId from the CONNECT packet is matched with the persisted credentials to authenticate the client.
The matching is based on the auto-generated credentialsId field from the MQTT client credentials.
The credentialsId is generated as follows:
- credentialsId =
username|$CLIENT_USERNAMEwhen only username is present; - credentialsId =
client_id|$CLIENT_IDwhen only client ID is present; - credentialsId =
mixed|$CLIENT_USERNAME|$CLIENT_IDwhen both username and client ID are present.
Where $CLIENT_USERNAME refers to the specified username, $CLIENT_ID refers to the specified client ID from the CONNECT packet.
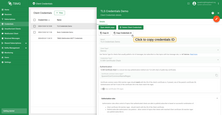
TLS Authentication
To enable TLS authentication, you must first enable the TLS listener so that the client’s certificate chain is involved in the authentication process.
After enabling the TLS listener, you need to do the following to enable TLS authentication:
- Set the
SECURITY_MQTT_SSL_ENABLEDenvironment variable totrue. - Create MQTT client credentials of type
X.509 Certificate Chainusing either the Web UI guide or the REST API guide. - Once the credentials are created, the
credentialsIdfield is auto-generated. See below for more information.
Credentials Matching
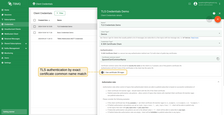
The “X.509 Certificate Chain” credentials have a “Use certificate CN regex” option that controls how credentials are matched.
-
When “Use certificate CN regex” is disabled: the “Certificate common name (CN)” must exactly match the CN of the client’s certificate or, if present, one of the parent’s certificates in the chain. Authentication will fail if none of the certificates have an exactly matching CN.
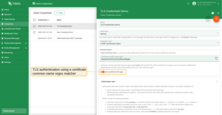
-
“Use certificate CN regex” is enabled: the “Certificate common name (CN) matcher regex” must match the CN of the client’s certificate or, if present, one of the parent’s certificates in the chain. Authentication will fail if no certificate in the chain matches the regex.
Credentials ID
The generation of credentialsId is done as follows:
- credentialsId =
ssl|$CERTIFICATE_COMMON_NAME; - credentialsId =
ssl|$CERTIFICATE_COMMON_NAME_REGEX.
Where $CERTIFICATE_COMMON_NAME is the common name of the certificate from the chain, $CERTIFICATE_COMMON_NAME_REGEX is a regex-based string
that should be matched with the certificate’s CN from the chain.
Strategies
TBMQ allows to set the authentication strategy by setting the environment variable SECURITY_MQTT_AUTH_STRATEGY, which has two possible values:
- BOTH (default). When both Basic and TLS authentications are enabled,
the MQTT Broker will prioritize
Basicauthentication. This means that if a client successfully authenticates with basic credentials, the system will not attempt to authenticate it usingTLSauthentication. However, ifBasicauthentication fails, the system will continue with the authentication process usingTLS. If one of the authentication types is disabled, the other type will be used. - SINGLE. The broker will only use one type of authentication depending on the listener to which the client is connected.
For example, if the client connects to the TCP listener, only
Basicauthentication will be used. On the other hand, if the client connects to the TLS listener, onlyTLSauthentication will be used.
Authorization
After the user has been authenticated, it is possible to restrict the client’s access to topics they can publish or subscribe to for both TLS and Basic authentications.
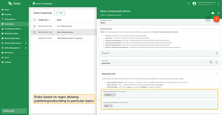
To provide flexible control over authorization rules, TBMQ uses regular expressions.
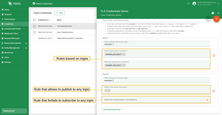
For example, to allow clients to publish or subscribe to all topics that begin with city/, an authorization rule should be created with the value city/.*.
Basic
For the Basic type, authorization is configured through the pubAuthRulePatterns and subAuthRulePatterns of the corresponding MQTT client credentials. Therefore, for each Basic MQTT client credential, you can configure the authorization rules for the topics that these clients can access.
The pubAuthRulePatterns and subAuthRulePatterns are based on regular expression syntax. For example,
1
2
3
4
{
"pubAuthRulePatterns": ["country/.*"],
"subAuthRulePatterns": ["city/.*"]
}
The following configuration allows clients to publish messages to topics that start with country/ and subscribe to topics that start with city/.
TLS
For TLS type, authorization is configured using the authRulesMapping field of the corresponding MQTT Client Credentials. Here is a model of the credentials value:
1
2
3
4
5
{
"certCnPattern": $certCnPattern,
"certCnIsRegex": $certCnIsRegex,
"authRulesMapping": $authRulesMapping
}
Where:
- $certCnPattern - the pattern for the common name that should be present in the certificate chain.
- $certCnIsRegex - option to control whether the common name (CN) pattern is treated as a regular expression (regex) for matching.
- $authRulesMapping - the mapping used to configure the access restrictions for different keywords.
For example,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
{ "example_1": { "pubAuthRulePatterns": ["example_pub_topic/.*"], "subAuthRulePatterns": ["example_sub_topic/.*"] }, "example_2": { "pubAuthRulePatterns": [".*"], "subAuthRulePatterns": [".*"] } }
This allows clients to connect with a certificate containing example_1 in its CN to publish only to topics that start with example_pub_topic/ and subscribe to topics that start with example_sub_topic/. Clients with a certificate containing example_2 are allowed to publish and subscribe to any topic.
Note: if either pubAuthRulePatterns or subAuthRulePatterns is set to null or an empty list ([]), the client will not be able to publish to or subscribe to any topics.